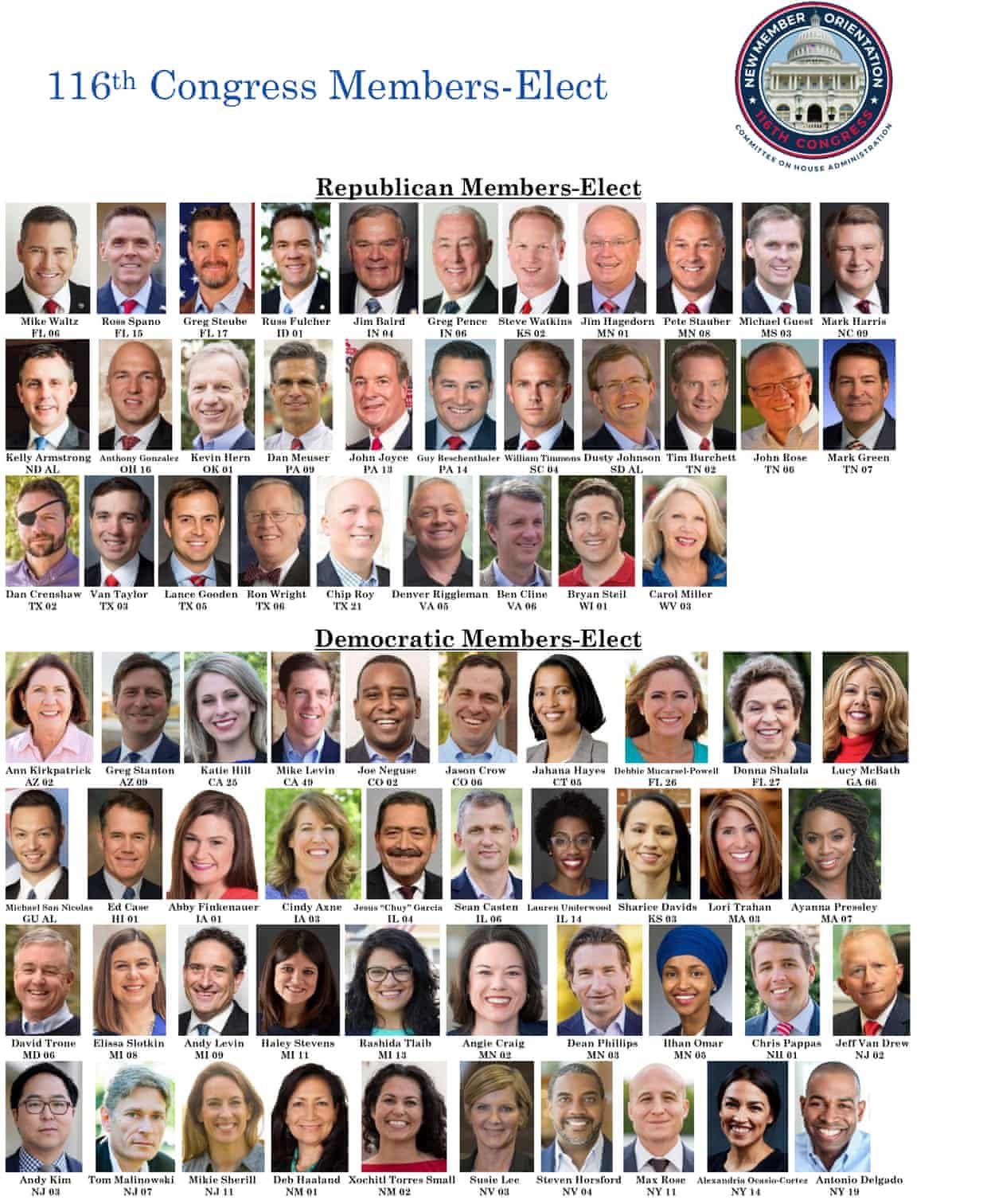
Table Of Content
Axiom won the $228.5 million contract in September to build the new moon suits. A few months later, Collins Aerospace nabbed the $97.2 million contract to configure new spacesuits for spacewalks outside the ISS. Astronauts will still wear a diaper-like garment during spacewalks that is a combination of commercial products stitched together for maximum absorption. Although space explorers generally prefer to not use it, it is there in the event they need to relieve themselves during a spacewalk that can last many hours. With a compression spacesuit we have to be careful because if I pick up something and my biceps increase in size, the compression level will be different.
Hard-shell suits
The last time humans set foot on the moon was more than 50 years ago, during the Apollo 17 mission in December 1972. And the last time NASA designed new spacesuits was roughly four decades ago, for astronauts to wear on the Space Shuttle. Today, those suits are the ones in use on the International Space Station (ISS). The first astronauts to walk on the moon since the 1970s will do so wearing sleek, new spacesuits. Axiom Space, the private company NASA tapped to design moonwalk suits for the Artemis 3 mission, unveiled its prototype on Wednesday at NASA’s Space Center Houston.
NASA’s New Spacesuit: It’s a Look

No one has ever died because of a faulty spacesuit, but that doesn’t mean current models are perfect. Whether it’s for launch into space or reentry back to Earth, or for an extravehicular activity (EVA, colloquially known as a spacewalk), astronauts have never been completely satisfied with the gear they are forced to put on for missions. Following Artemis III, the agency will compete future Artemis mission services under the Exploration Extravehicular Activity Services (xEVAS) contract.
Astronaut Glove Challenge
The primary components of the pressure garment are the upper torso, helmet, lower torso and cooling garment. The lower section of the suit is made up of spacesuit pants, boots and the lower half of the waist closure. A metal body-seal closure connects the lower torso to the hard upper torso. On the new suits that will be used for lunar surface missions, the lower torso includes advanced materials and joint interfaces that allow bending and rotating at the hips, bending at the knees, and hiking-style boots.
The Space Suit Path to the Lunar South Pole
In order to retain a better sense of touch for the astronauts, the fingertips of the gloves were made of silicone. With the shuttle program, it became necessary to be able to operate spacecraft modules, so the ACES suits featured gripping on the gloves. EMU gloves, which are used for spacewalks, are heated to keep the astronaut's hands warm.
A spacesuit designer on what to wear to the moon
However, 21st century moonwalkers will be able to accomplish much more complex tasks than their predecessors, thanks to strides in technological advances that started even before the Apollo program. The first full-pressure suits for use at extreme altitudes were designed by individual inventors as early as the 1930s. The first space suit worn by a human in space was the Soviet SK-1 suit worn by Yuri Gagarin in 1961. Spacesuits similar to the Apollo suits were used on the Skylab space station. Like the Gemini suits, the Skylab suits connected to life support systems on the spacecraft via an umbilical.
MIT Technology Review
Prada to design NASA's new next-gen spacesuits - ABC News
Prada to design NASA's new next-gen spacesuits.
Posted: Fri, 06 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
They’re tailored to offer astronauts more flexibility and mobility when they set foot on the lunar South Pole, which is scheduled to take place as soon as 2025. Is it the shoulders, where a few inches’ difference in joint placement can lead to a repetitive stress injury? Is it the outer layer, which must protect its wearer from micrometeorites, tiny flecks of metal, rock, or paint hurtling thousands of miles per hour through space?
At altitudes above the Armstrong limit, around 19,000 m (62,000 ft), water boils at body temperature and pressurized suits are needed. The first piece of a spacesuit that astronauts put on is a special cooling garment made of a stretchy spandex material and water tubes. About 300 feet of tubes are woven into this tight-fitting piece of clothing that covers the entire body except for the head, hands and feet. Chilled water flows through the tubes near the spacewalker’s skin to regulate body temperature and remove extra heat during the spacewalk, which typically lasts multiple hours. Vents in the garment draw sweat away from the astronaut’s body and help with circulation inside the spacesuit garment. Before donning the actual spacesuit, the first piece that astronauts put on is a special cooling garment made of a stretchy spandex material and water tubes.
“Dust is going to be a pretty tricky problem to deal with,” Ralston said. That includes ways to prevent dust from adhering to the suit in the first place, and then, when dust dues stick to it, keep it from coming off when the astronauts go back inside their lunar lander. The full suit, which includes an integrated shoe, weighs about 20 pounds with all its accessories – about 10 pounds lighter than the launch-and-entry suits worn by space shuttle astronauts.
The prototype includes a dark gray cover, which was designed by costume designer Esther Marquis, who worked on the TV series For All Mankind, but the actual suit will be white for thermal reasons. The moon’s surface hasn’t been exposed to the kind of weathering Earth’s geology has faced. As a result, the lunar soil is very coarse and jagged, and it sticks to everything (yeah, I know I sound like Anakin Skywalker). It contaminates inner layers of the garment and any parts that are supposed to detach, and causes general wear and tear to the exterior of the suits. The xEMU has bearings that are lighter and hew closer to the joints than ones used for previous EMUs.
It features a soft torso versus the hard torsos seen in previous NASA EVA space suits, which reduces mass.[60] It has been labeled the "Buzz Lightyear suit" due to its green streaks for a design. Axiom is best known for private astronaut missions to the ISS and plans to add commercial modules to the station as a precursor to its own commercial space station. Mark Greeley, program manager for extravehicular activity at Axiom, said the company will use a similar design for suits it plans to develop for space station spacewalks, with differences in elements like boots and gloves. Artemis astronauts will be more nimble than ever before with mobility enhancements in the new suits. Bunny-hopping Apollo astronauts are fun to watch, but the exertion required to move around that way was more than NASA would have liked for their explorers who were 250,000 miles from home. The pressure garment is the human shaped portion of the spacesuit that enables astronaut mobility and protects their body from the external environment including, extreme temperatures, radiation, micrometeoroids, and reduced atmospheric pressure.
The space agency hopes to establish the first long-term presence on the moon and, using knowledge gleaned from those efforts, send the first humans to Mars. Artemis 1 successfully launched the uncrewed Orion spacecraft into orbit around the moon in November, after several delays. Artemis 2, which is scheduled for 2024, aims to fly four astronauts around the moon.
The flexible parts of the suit are made from as many as 16 layers of material. The layers perform different functions, from keeping oxygen within the spacesuit to protecting from space dust. Closest to the astronaut’s skin, the cooling garment makes up the first three layers. On top of this garment is the bladder layer that is filled with gas to create proper pressure for the body and holds in the oxygen for breathing. The next layer holds the bladder layer to the correct shape around the astronaut’s body. The next several layers are insulation and act like a thermos to help maintain the temperature inside the suit.